We Are Going To Cover Important Information About Orthopedics. The pterygoid fovea is located on the condylar.

Lateral And Medial Pterygoid Diagram Quizlet
A broad thin plate that forms the lateral part of the pterygoid process and gives attachment to the lateral pterygoid muscle on its lateral surface and to the medial pterygoid muscle on its medial surface.
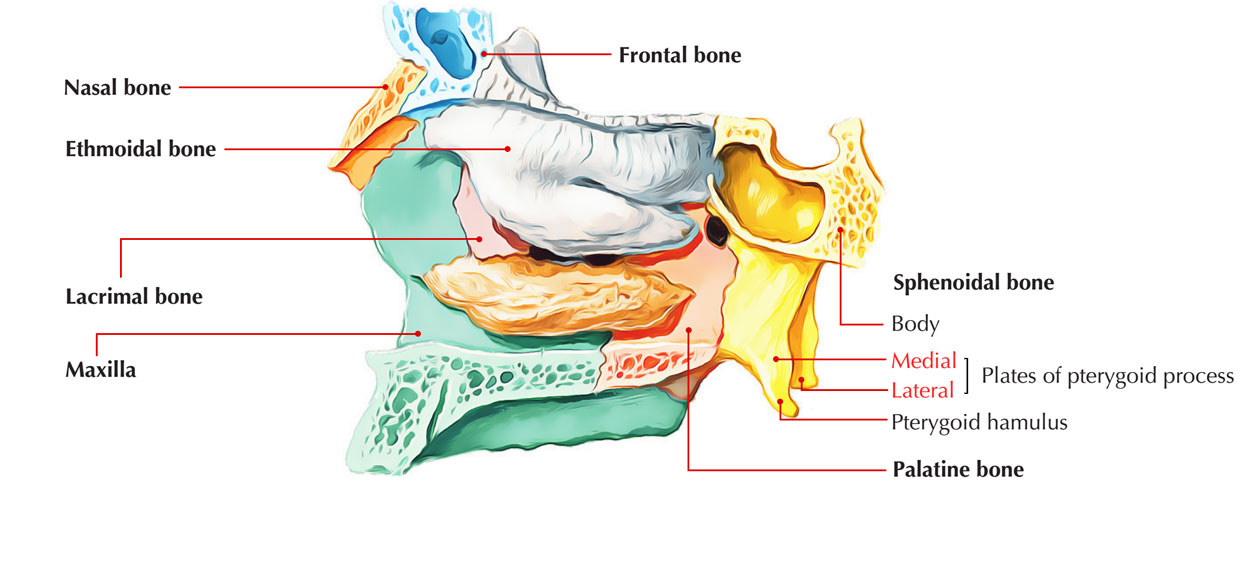
. Each process consists of a medial pterygoid plate and a lateral pterygoid plate the latter of which serve as the origins of the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles. The pterygoid hamulus is a hook-shaped bony process located bilaterally on each medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone posterior and medial to each maxillary tuberosity. The suspected mechanism is due to force transduction through the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles when acute displacing force is placed on the mandible.
The thickness of the pterygomaxillary region T was significantly greater in the disjunction. The medial pterygoid muscle is a thick and square shaped muscle. The medial pterygoid plate is narrower and longer while the lateral pterygoid plate is broad thin and everted.
Ad Hurry Up Now and Discover the Important Information about Orthopedics. It curves lateralward at its lower extremity into a hook-like process the pterygoid hamulus around which the tendon of the Tensor veli palatini glides. The maxillary tuberosity separated from the medial and lateral pterygoid plates during the procedure was grouped into the disjunction group 24 of 30 80 and the pterygoid plates fractured were grouped into the fracture group 6 of 30 20.
These movements maximize the efficiency of the teeth while chewing or grinding foods of various consistencies. Called also lateral pterygoid plate. Aassits the lateral pterygoids in moving the jaw side-to-side.
Deep head medial side of lateral pterygoid plate and fossa between medial and lateral plates. ACTION Elevates the mandible and assits in closing the jaw. The lateral pterygoid allows the jaw to move in a horizontal direction during mastication.
Each pterygoid process projects inferiorly from the junction of the body and greater wing of the sphenoid bone and bifurcates into a medial pterygoid plate and a lateral pterygoid plate. The superficial head is attached to the maxillary tuberosity and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. It belongs to the group of masticatory muscles along with the lateral pterygoid masseter and temporal muscles.
A broad thin plate that forms the lateral part of the pterygoid process and gives attachment to the lateral pterygoid muscle on its lateral surface and to the medial pterygoid muscle on its medial surface. At the inferior tip of the medial pterygoid plate is the small hook-shaped process the pterygoid hamulus. Bilaterally the medial pterygoid is one of the muscles of mastication.
The medial pterygoid muscle has a superficial and a deep head which arise from different areas of the jaw. Pterygoid hamular bursitis is a rare craniofacial pain syndrome used to describe palatal and pharyngeal pain due to an enlarged pterygoid hamulus. The lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid or lateral lamina of pterygoid process is broad thin and everted and forms the lateral part of a horseshoe like process that extends from the inferior aspect of the sphenoid bone and serves as the origin of the lateral pterygoid muscle which functions in allowing the mandible to move in a.
The pharyngeal aponeurosis is attached to the entire length of the posterior edge of the medial plate and the constrictor pharyngis superior takes origin from its lower third. - CT features of isolate pterygoid fracture. The medial pterygoid plate or medial pterygoid lamina of the sphenoid bone is a horse-shoe shaped process that arises from its underside.
The superior head of the lateral pterygoid originates from the infratemporal surface and crest of the greater wing of the sphenoid. In patients with identified isolated pterygoid plate factures a dedicated CT of the mandible may be indicated to assess for associated mandibular fracture even in patients whose clinical. The inferior head of this muscle originates from the lateral surface of the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
The medial pterygoid plate is narrower and longer than the lateral. Lateral pterygoid muscle has its the lower part connect to the lateral part of the lateral pterygoid plate. The lateral pterygoid muscle via its lower head separates the two distinct heads.
The lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone gives rise to the deep head. The medial pterygoid along with the masseter allows the jaw to move in a vertical direction as it contracts and relaxes. The suspected mechanism is due to force transduction through the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles when acute displacing force is placed on the mandible.
The spaces separated the medial and lateral plate are pterygoid. Called also lateral pterygoid plate. The deep head is the major component and is attached to the medial aspect of the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
Force transduction through the pterygoid muscles. Both pterygoids protract the mandible and move it from side to side during chewing. Superior pharyngeal constrictor is attached towards inferior end of the medial pterygoid plate.
Medial pterygoid muscle is attached towards medial part of the lateral pterygoid plate. Medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads. Moreover what artery supplies the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles.
A variable pterygospinous process on its irregular posterior border is connected by a ligament sometimes ossified to the sphenoid spine 1. A long narrow plate that forms the medial part of the pterygoid process terminates in the pterygoid hamulus and forms with its lateral. Superficial head from the pyramidal process of the palatine bone and the tuberosity of the maxilla.
The smaller superficial head has its origin mainly from the maxillary tuberosity with some fibers arising from the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. The deep head of the muscle originates from the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone. Origin and insertion of medial pterygoid by Anatomy Next Action.
The lateral surfaceof this plate forms part of the pterygoid fossa the medial surface constitutes the lateral boundary of the choana or posterior aperture of the. Medial pterygoid muscles arise from the lateral pterygoid plates of the sphenoid bone and insert on the mandible. Although having different origins both heads insert on the inner.
INSERTION Medial aspect of angle of mandible. Medial pterygoid is a thick quadrilateral muscle that connects the mandible with maxilla sphenoid and palatine bones. In patients with identified isolated pterygoid plate factures a dedicated CT of the mandible may be indicated to assess for associated mandibular fracture even in patients whose clinical examinations have had.
It has two heads of origin. Unilateral no involvement of medial plate Vertical fracture of lateral pterygoid plate - Proposed mechanism. Deep head from the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate and the fossa separating this and the medial plate.
The medial pterygoid inserts on the pterygoid tuberosity of the mandible and medial inner surface of the mandibular ramus. Tuberosity of maxilla and pyramidal process of palatine bone. The medial pterygoid muscle is situated underneath the lateral pterygoid.
The lateral pterygoid inserts on the pterygoid fovea of the mandible. The maxillary tuberosity and the palatine bones pyramidal process give rise to the superficial head. - An isolated lateral pterygoid plate fracture suggests the presence of a mandible fracture.
The medial pterygoid also elevates the mandible. It originates from two sites.

Anatomy Trains Australia Nz Friday Anatomy Fact The Beautiful Pterygoids With The Coolest Name I Have A List Of Favourite Muscles And This One Is Top Of My List Along

Infratemporal Fossa Lo Pterygoid Plates Youtube

The Art And Science Of Kinesiology Very Cool View Of The Pterygoid Muscles A Posterior View Of The Lateral And Medial Pterygoids Muscles Of The Tmj For Mastication They Both Attach
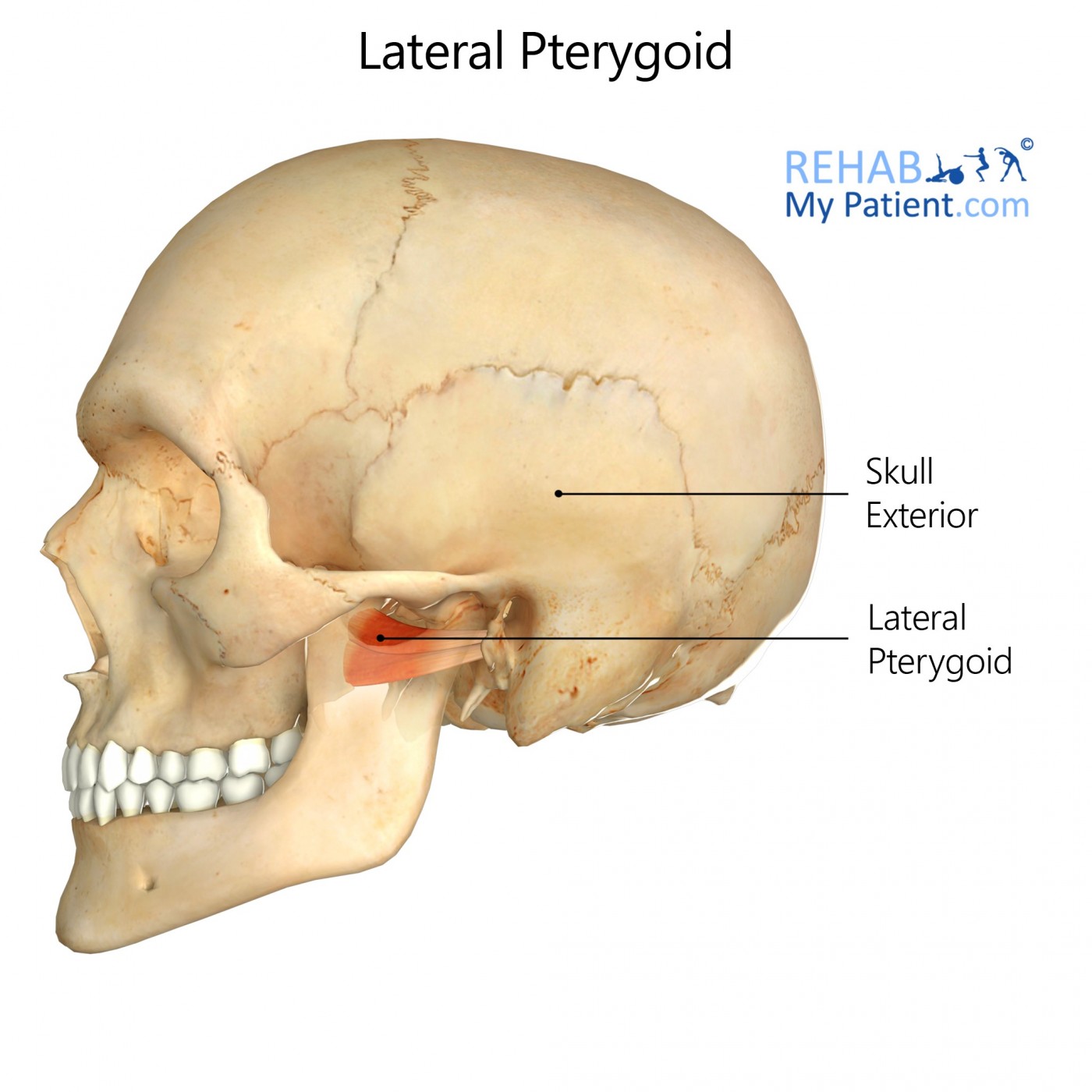
Lateral Pterygoid Rehab My Patient
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14110/Pterygoid_muscles.png)
Medial And Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Anatomy And Function Kenhub
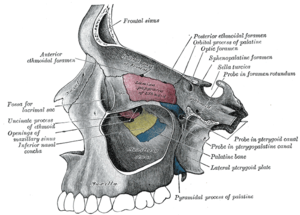
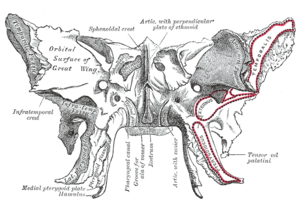
0 comments
Post a Comment